Set up app links for Android
Learn how to set up app links for an Android application built with Flutter.
Deep linking is a mechanism for launching an app with a URI. This URI contains scheme, host, and path, and opens the app to a specific screen.
An app link is a type of deep link that uses
http or https and is exclusive to Android devices.
Setting up app links requires one to own a web domain. Otherwise, consider using Firebase Hosting or GitHub Pages as a temporary solution.
Once you've set up your deep links, you can validate them. To learn more, see Validate deep links.
1. Customize a Flutter application
#
Write a Flutter app that can handle an incoming URL.
This example uses the go_router package to handle the routing.
The Flutter team maintains the go_router package.
It provides a simple API to handle complex routing scenarios.
-
To create a new application, type
flutter create <app-name>:flutter create deeplink_cookbook -
To include
go_routerpackage in your app, add a dependency forgo_routerto the project:To add the
go_routerpackage as a dependency, runflutter pub add:flutter pub add go_router -
To handle the routing, create a
GoRouterobject in themain.dartfile:main.dartdartimport 'package:flutter/material.dart'; import 'package:go_router/go_router.dart'; void main() => runApp(MaterialApp.router(routerConfig: router)); /// This handles '/' and '/details'. final router = GoRouter( routes: [ GoRoute( path: '/', builder: (_, _) => Scaffold( appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('Home Screen')), ), routes: [ GoRoute( path: 'details', builder: (_, _) => Scaffold( appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('Details Screen')), ), ), ], ), ], );
2. Modify AndroidManifest.xml
#Open the Flutter project with VS Code or Android Studio.
Navigate to
android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xmlfile.-
Add the following metadata tag and intent filter inside the
<activity>tag with.MainActivity.Replace
example.comwith your own web domain.xml<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true"> <action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" /> <data android:scheme="http" android:host="example.com" /> <data android:scheme="https" /> </intent-filter>
3. Hosting assetlinks.json file
#
Host an assetlinks.json file in using a web server
with a domain that you own. This file tells the
mobile browser which Android application to open instead
of the browser. To create the file,
get the package name of the Flutter app you created in
the previous step and the sha256 fingerprint of the
signing key you will be using to build the APK.
Package name
#
Locate the package name in AndroidManifest.xml,
the package property under <manifest> tag.
Package names are usually in the format of com.example.*.
sha256 fingerprint
#The process might differ depending on how the apk is signed.
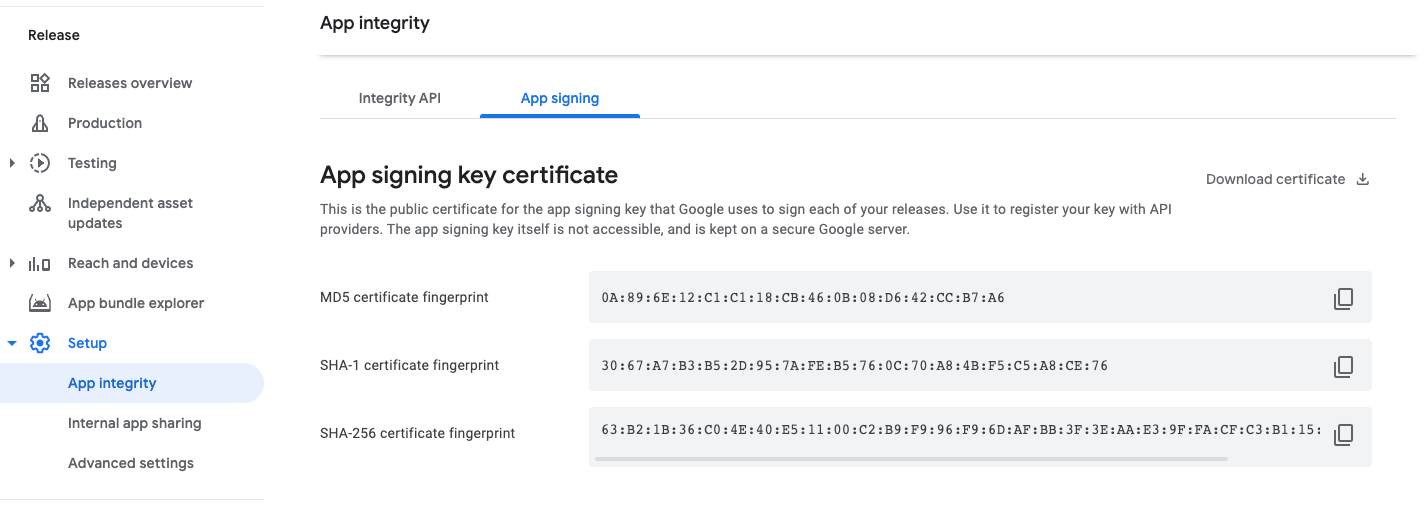
Using google play app signing
#You can find the sha256 fingerprint directly from play developer console. Open your app in the play console, under Release> Setup > App Integrity> App Signing tab:
Using local keystore
#If you are storing the key locally, you can generate sha256 using the following command:
keytool -list -v -keystore <path-to-keystore>
assetlinks.json
#The hosted file should look similar to this:
[{
"relation": ["delegate_permission/common.handle_all_urls"],
"target": {
"namespace": "android_app",
"package_name": "com.example.deeplink_cookbook",
"sha256_cert_fingerprints":
["FF:2A:CF:7B:DD:CC:F1:03:3E:E8:B2:27:7C:A2:E3:3C:DE:13:DB:AC:8E:EB:3A:B9:72:A1:0E:26:8A:F5:EC:AF"]
}
}]
Set the
package_namevalue to your Android application ID.-
Set sha256_cert_fingerprints to the value you got from the previous step.
-
Host the file at a URL that resembles the following:
<webdomain>/.well-known/assetlinks.json Verify that your browser can access this file.
Testing
#
You can use a real device or the Emulator to test an app link,
but first make sure you have executed flutter run at least once on
the devices. This ensures that the Flutter application is installed.

To test only the app setup, use the adb command:
adb shell 'am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW \
-c android.intent.category.BROWSABLE \
-d "http://<web-domain>/details"' \
<package name>
To test both web and app setup, you must click a link directly through web browser or another app. One way is to create a Google Doc, add the link, and tap on it.
If everything is set up correctly, the Flutter application launches and displays the details screen:

Appendix
#Source code: deeplink_cookbook
Unless stated otherwise, the documentation on this site reflects Flutter 3.41.2. Page last updated on 2025-10-30. View source or report an issue.