Differentiate between ephemeral state and app state
How to tell the difference between ephemeral and app state.
This doc introduces app state, ephemeral state, and how you might manage each in a Flutter app.
In the broadest possible sense, the state of an app is everything that exists in memory when the app is running. This includes the app's assets, all the variables that the Flutter framework keeps about the UI, animation state, textures, fonts, and so on. While this broadest possible definition of state is valid, it's not very useful for architecting an app.
First, you don't even manage some state (like textures). The framework handles those for you. So a more useful definition of state is "whatever data you need in order to rebuild your UI at any moment in time". Second, the state that you do manage yourself can be separated into two conceptual types: ephemeral state and app state.
Ephemeral state
#Ephemeral state (sometimes called UI state or local state) is the state you can neatly contain in a single widget.
This is, intentionally, a vague definition, so here are a few examples.
-
current page in a
PageView - current progress of a complex animation
- current selected tab in a
BottomNavigationBar
Other parts of the widget tree seldom need to access this kind of state. There is no need to serialize it, and it doesn't change in complex ways.
In other words, there is no need to use state management techniques
(ScopedModel, Redux, etc.) on this kind of state.
All you need is a StatefulWidget.
Below, you see how the currently selected item in a bottom navigation bar is
held in the _index field of the _MyHomepageState class.
In this example, _index is ephemeral state.
class MyHomepage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomepage({super.key});
@override
State<MyHomepage> createState() => _MyHomepageState();
}
class _MyHomepageState extends State<MyHomepage> {
int _index = 0;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return BottomNavigationBar(
currentIndex: _index,
onTap: (newIndex) {
setState(() {
_index = newIndex;
});
},
// ... items ...
);
}
}
Here, using setState() and a field inside the StatefulWidget's State
class is completely natural. No other part of your app needs to access
_index. The variable only changes inside the MyHomepage widget.
And, if the user closes and restarts the app,
you don't mind that _index resets to zero.
App state
#State that is not ephemeral, that you want to share across many parts of your app, and that you want to keep between user sessions, is what we call application state (sometimes also called shared state).
Examples of application state:
- User preferences
- Login info
- Notifications in a social networking app
- The shopping cart in an e-commerce app
- Read/unread state of articles in a news app
For managing app state, you'll want to research your options. Your choice depends on the complexity and nature of your app, your team's previous experience, and many other aspects. Read on.
There is no clear-cut rule
#
To be clear, you can use State and setState() to manage all of
the state in your app. In fact, the Flutter team does this in many
simple app samples (including the starter app that you get with every
flutter create).
It goes the other way, too. For example, you might decide that—in
the context of your particular app—the selected tab in a bottom
navigation bar is not ephemeral state. You might need to change it
from outside the class, keep it between sessions, and so on.
In that case, the _index variable is app state.
There is no clear-cut, universal rule to distinguish whether a particular variable is ephemeral or app state. Sometimes, you'll have to refactor one into another. For example, you'll start with some clearly ephemeral state, but as your application grows in features, it might need to be moved to app state.
For that reason, take the following diagram with a large grain of salt:
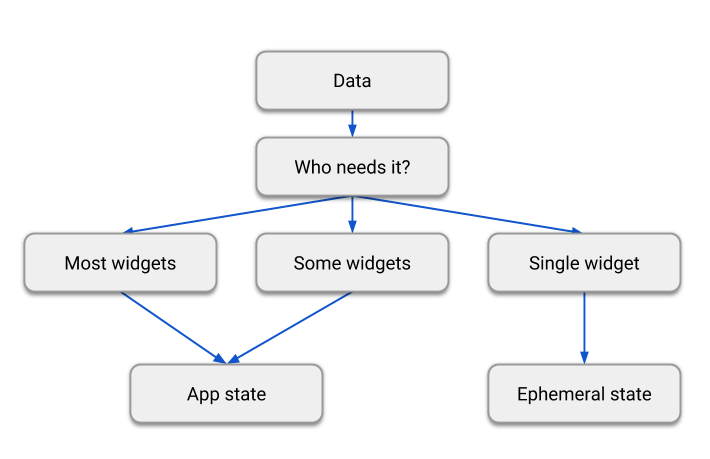
When asked about React's setState versus Redux's store, the author of Redux, Dan Abramov, replied:
"The rule of thumb is: Do whatever is less awkward."
In summary, there are two conceptual types of state in any Flutter app.
Ephemeral state can be implemented using State and setState(),
and is often local to a single widget. The rest is your app state.
Both types have their place in any Flutter app, and the split between
the two depends on your own preference and the complexity of the app.
Unless stated otherwise, the documentation on this site reflects Flutter 3.41.2. Page last updated on 2025-04-10. View source or report an issue.