Persistent storage architecture: Key-value data
Save application data to a user's on-device key-value store.
Most Flutter applications, no matter how small or big they are, require storing data on the user’s device at some point, such as API keys, user preferences or data that should be available offline.
In this recipe, you will learn how to integrate persistent storage for key-value data in a Flutter application that uses the recommended Flutter architecture design. If you aren’t familiar with storing data to disk at all, you can read the Store key-value data on disk recipe.
Key-value stores are often used for saving simple data, such as app configuration, and in this recipe you’ll use it to save Dark Mode preferences. If you want to learn how to store complex data on a device, you’ll likely want to use SQL. In that case, take a look at the cookbook recipe that follows this one called Persistent storage architecture: SQL.
Example application: App with theme selection
#The example application consists of a single screen with an app bar at the top, a list of items, and a text field input at the bottom.
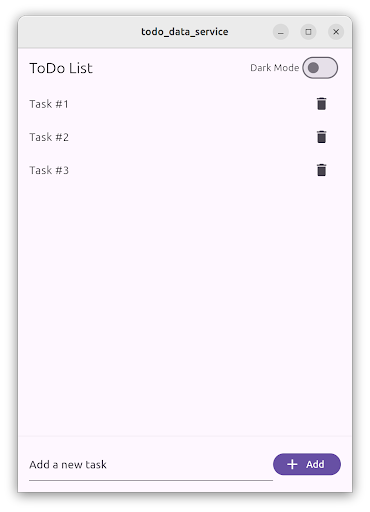
In the AppBar,
a Switch allows users to change between dark and light theme modes.
This setting is applied immediately and it’s stored in the device
using a key-value data storage service.
The setting is restored when the user starts the application again.
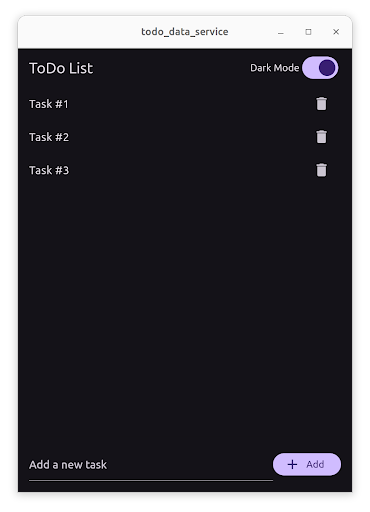
Storing theme selection key-value data
#This functionality follows the recommended Flutter architecture design pattern, with a presentation and a data layer.
-
The presentation layer contains the
ThemeSwitchwidget and theThemeSwitchViewModel. -
The data layer contains the
ThemeRepositoryand theSharedPreferencesService.
Theme selection presentation layer
#
The ThemeSwitch is a StatelessWidget that contains a Switch widget.
The state of the switch is represented
by the public field isDarkMode in the ThemeSwitchViewModel.
When the user taps the switch,
the code executes the command toggle in the view model.
class ThemeSwitch extends StatelessWidget {
const ThemeSwitch({super.key, required this.viewmodel});
final ThemeSwitchViewModel viewmodel;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
child: Row(
children: [
const Text('Dark Mode'),
ListenableBuilder(
listenable: viewmodel,
builder: (context, _) {
return Switch(
value: viewmodel.isDarkMode,
onChanged: (_) {
viewmodel.toggle.execute();
},
);
},
),
],
),
);
}
}
The ThemeSwitchViewModel implements a view model
as described in the MVVM pattern.
This view model contains the state of the ThemeSwitch widget,
represented by the boolean variable _isDarkMode.
The view model uses the ThemeRepository
to store and load the dark mode setting.
It contains two different command actions:
load, which loads the dark mode setting from the repository,
and toggle, which switches the state between dark mode and light mode.
It exposes the state through the isDarkMode getter.
The _load method implements the load command.
This method calls ThemeRepository.isDarkMode
to obtain the stored setting and calls notifyListeners() to refresh the UI.
The _toggle method implements the toggle command.
This method calls ThemeRepository.setDarkMode
to store the new dark mode setting.
As well, it changes the local state of _isDarkMode
then calls notifyListeners() to update the UI.
class ThemeSwitchViewModel extends ChangeNotifier {
ThemeSwitchViewModel(this._themeRepository) {
load = Command0(_load)..execute();
toggle = Command0(_toggle);
}
final ThemeRepository _themeRepository;
bool _isDarkMode = false;
/// If true show dark mode
bool get isDarkMode => _isDarkMode;
late final Command0<void> load;
late final Command0<void> toggle;
/// Load the current theme setting from the repository
Future<Result<void>> _load() async {
final result = await _themeRepository.isDarkMode();
if (result is Ok<bool>) {
_isDarkMode = result.value;
}
notifyListeners();
return result;
}
/// Toggle the theme setting
Future<Result<void>> _toggle() async {
_isDarkMode = !_isDarkMode;
final result = await _themeRepository.setDarkMode(_isDarkMode);
notifyListeners();
return result;
}
}
Theme selection data layer
#
Following the architecture guidelines,
the data layer is split into two parts:
the ThemeRepository and the SharedPreferencesService.
The ThemeRepository is the single source of truth
for all the theming configuration settings,
and handles any possible errors coming from the service layer.
In this example,
the ThemeRepository also exposes the dark mode setting
through an observable Stream.
This allows other parts of the application
to subscribe to changes in the dark mode setting.
The ThemeRepository depends on SharedPreferencesService.
The repository obtains the stored value from the service,
and stores it when it changes.
The setDarkMode() method passes the new value to the StreamController,
so that any component listening to the observeDarkMode stream
class ThemeRepository {
ThemeRepository(this._service);
final _darkModeController = StreamController<bool>.broadcast();
final SharedPreferencesService _service;
/// Get if dark mode is enabled
Future<Result<bool>> isDarkMode() async {
try {
final value = await _service.isDarkMode();
return Result.ok(value);
} on Exception catch (e) {
return Result.error(e);
}
}
/// Set dark mode
Future<Result<void>> setDarkMode(bool value) async {
try {
await _service.setDarkMode(value);
_darkModeController.add(value);
return Result.ok(null);
} on Exception catch (e) {
return Result.error(e);
}
}
/// Stream that emits theme config changes.
/// ViewModels should call [isDarkMode] to get the current theme setting.
Stream<bool> observeDarkMode() => _darkModeController.stream;
}
The SharedPreferencesService wraps
the SharedPreferences plugin functionality,
and calls to the setBool() and getBool() methods
to store the dark mode setting,
hiding this third-party dependency from the rest of the application
class SharedPreferencesService {
static const String _kDarkMode = 'darkMode';
Future<void> setDarkMode(bool value) async {
final prefs = await SharedPreferences.getInstance();
await prefs.setBool(_kDarkMode, value);
}
Future<bool> isDarkMode() async {
final prefs = await SharedPreferences.getInstance();
return prefs.getBool(_kDarkMode) ?? false;
}
}
Putting it all together
#
In this example,
the ThemeRepository and SharedPreferencesService are created
in the main() method
and passed to the MainApp as constructor argument dependency.
void main() {
// ···
runApp(
MainApp(
themeRepository: ThemeRepository(SharedPreferencesService()),
// ···
),
);
}
Then, when the ThemeSwitch is created,
also create ThemeSwitchViewModel
and pass the ThemeRepository as dependency.
ThemeSwitch(
viewmodel: ThemeSwitchViewModel(widget.themeRepository),
),
The example application also includes the MainAppViewModel class,
which listens to changes in the ThemeRepository
and exposes the dark mode setting to the MaterialApp widget.
class MainAppViewModel extends ChangeNotifier {
MainAppViewModel(this._themeRepository) {
_subscription = _themeRepository.observeDarkMode().listen((isDarkMode) {
_isDarkMode = isDarkMode;
notifyListeners();
});
_load();
}
final ThemeRepository _themeRepository;
StreamSubscription<bool>? _subscription;
bool _isDarkMode = false;
bool get isDarkMode => _isDarkMode;
Future<void> _load() async {
final result = await _themeRepository.isDarkMode();
if (result is Ok<bool>) {
_isDarkMode = result.value;
}
notifyListeners();
}
@override
void dispose() {
_subscription?.cancel();
super.dispose();
}
}
ListenableBuilder(
listenable: _viewModel,
builder: (context, child) {
return MaterialApp(
theme: _viewModel.isDarkMode ? ThemeData.dark() : ThemeData.light(),
home: child,
);
},
child: //...
)
Unless stated otherwise, the documentation on this site reflects Flutter 3.41.2. Page last updated on 2025-10-30. View source or report an issue.