DevTools
Learn to use the Dart DevTools when developing Flutter apps.
Learn to use the widget inspector and property editor to debug layout issues and experiment with properties in real-time.
What you'll accomplish
Steps
1
Introduction
Introduction
As your Flutter app grows in complexity, it becomes more important to understand how each of the widget properties affects the UI. The Dart and Flutter DevTools provide you with two particularly useful features: the widget inspector and the property editor.
First, launch DevTools by running the following commands while your app is running in debug mode:
dart devtools
2
The widget inspector
The widget inspector
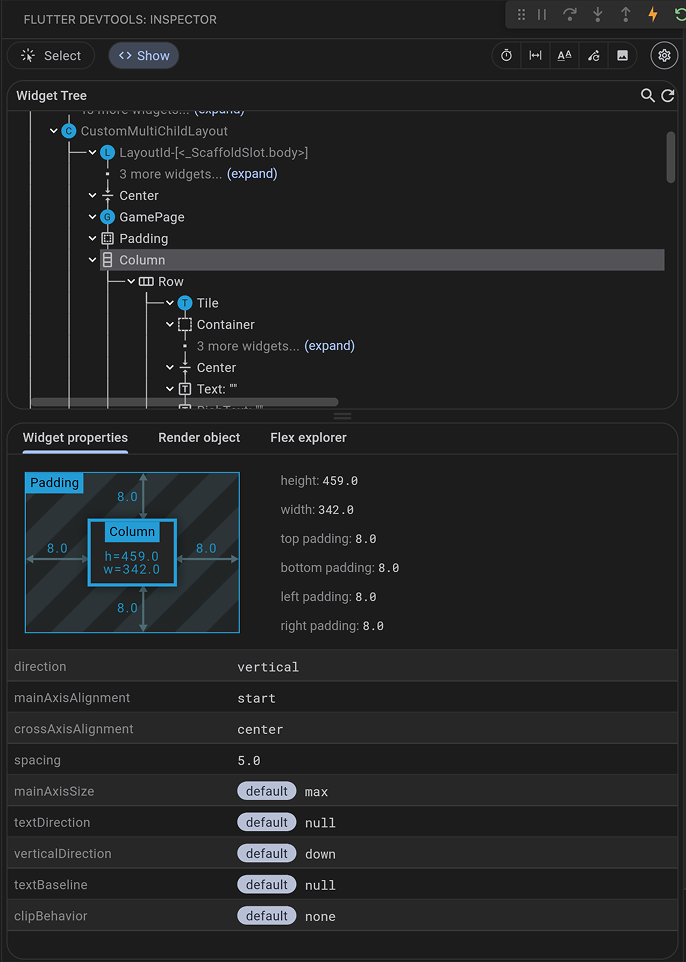
The widget inspector allows you to visualize and explore your widget tree. It helps you understand the layout of your UI and identifies which widgets are responsible for different parts of the screen. Running against the app you've built so far, the inspector looks like this:
Consider the GamePage widget you created in this section:
class GamePage extends StatelessWidget {
const GamePage({super.key});
final Game _game = Game();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child: Column(
spacing: 5.0,
children: [
for (var guess in _game.guesses)
Row(
spacing: 5.0,
children: [
for (var letter in guess) Tile(letter, )
]
),
],
),
);
}
}
And how it's used in MainApp:
class MainApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MainApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body: Center(child: GamePage()),
),
);
}
}
In the widget inspector, you should see a tree of
exactly the same widgets that are in your code:
MaterialApp as the root, with Scaffold as its
home,
an AppBar as its appBar, and so on down the entire tree to
the Row widgets with Tile children.
You can select any widget in the tree to see its properties and
even jump to its source code in your IDE.
3
Debugging layout issues
Debugging layout issues
The widget inspector is perhaps most useful for debugging layout issues.
In certain situations,
a widget's constraints are unbounded, or infinite.
This means that either
the maximum width or the maximum height is set to double.infinity.
A widget that tries to be as big as possible won't function usefully when
given an unbounded constraint and, in debug mode, throws an exception.
The most common case where a render box ends up with an unbounded
constraint is within a flex box widget (Row
or Column),
and within a scrollable region,
such as a ListView
or ScrollView
subclasses.
ListView, for example, tries to expand to
fit the space available in its cross-direction. Such as if
it's a vertically scrolling block that tries to be as wide as its parent.
If you nest a vertically scrolling ListView inside
a horizontally scrolling ListView, the inner list tries to
be as wide as possible, which is infinitely wide, since the
outer one is scrollable in that direction.
Perhaps the most common error you'll run into while building a Flutter application is due to incorrectly using layout widgets. This error is referred to as the "unbounded constraints" error.
Watch the following video to get an understanding of how to spot and resolve this issue.
4
The property editor
The property editor
When you select a widget in the widget inspector, the property editor displays all the properties of that selected widget. This is a powerful tool for understanding why a widget looks the way it does and for experimenting with property value changes in real-time.
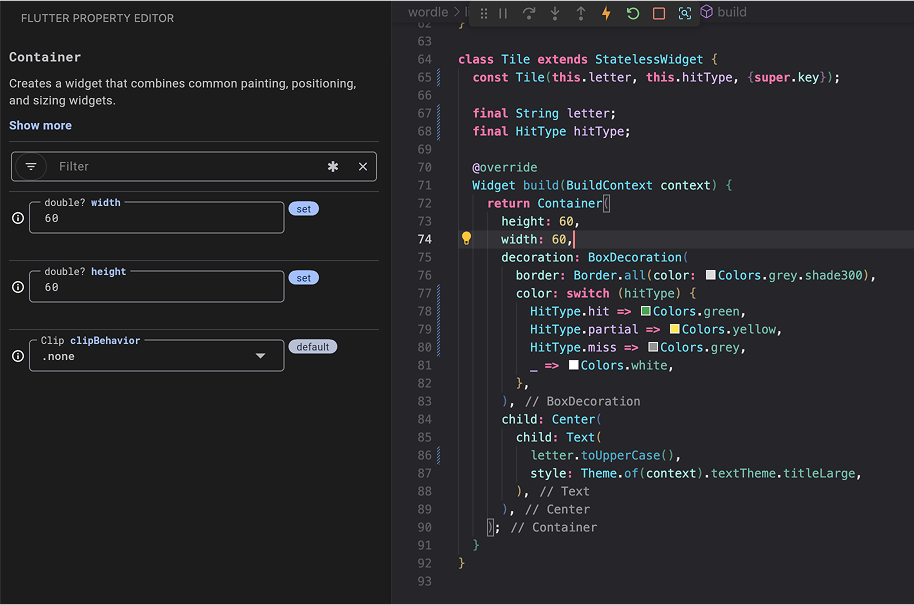
Look at the Tile widget's build method from earlier:
class Tile extends StatelessWidget {
const Tile(required this.letter, required hitType, {super.key});
final String letter;
final HitType hitType;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
width: 60,
height: 60,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
border: Border.all(color: Colors.grey.shade300),
color: switch (hitType) {
HitType.hit => Colors.green,
HitType.partial => Colors.yellow,
HitType.miss => Colors.grey,
_ => Colors.white,
},
),
);
}
}
If you select a Tile widget in the widget inspector,
the property editor would show you its
width (60), height (60), and the decoration
property.
You could then expand the BoxDecoration to
see the border and color properties.
For many properties, you can even
modify their values directly within the property editor.
For example, to quickly test how a different width or height
would look
for your Container in the Tile widget,
change the numerical value in the property editor.
Then instantly see the update on your running app without
needing to recompile or even hot reload.
This allows for rapid iteration on UI design.
5
Review
Review
What you accomplished
Here's a summary of what you built and learned in this lesson.Explored your app's widget tree with the widget inspector
The widget inspector lets you visualize your entire widget tree, select any widget to view its properties, and jump directly to its source code. It's an essential tool for understanding your app's structure.
Learned about common layout issues
You learned about unbounded constraints, one of the most common errors hit in Flutter development. This happens when widgets like
Row, Column, or ListView receive infinite constraints. Now you can recognize and fix these issues when they occur.
Learned about common layout issues
You learned about unbounded constraints, one of the most common errors hit in Flutter development. This happens when widgets like
Row, Column, or ListView receive infinite constraints. Now you can recognize and fix these issues when they occur.
Experimented with properties in real-time
The property editor shows all properties of a selected widget and lets you modify values instantly with no recompiling or hot reload needed. This enables rapid iteration when fine-tuning your UI.
6
Test yourself
Test yourself
DevTools Quiz
1 / 2-
Using too many StatefulWidgets in the widget tree.
Not quite
StatefulWidget usage doesn't cause unbounded constraints.
-
Placing a widget that tries to expand infinitely inside a scrollable or flex container without proper constraints.
That's right!
Widgets like ListView inside a Row, or nested scrollables, can receive infinite constraints and fail.
-
Forgetting to call setState after changing data.
Not quite
Missing setState causes UI not to update, not constraint errors.
-
Using Container without specifying a color.
Not quite
Color is optional and unrelated to layout constraints.
-
Automatically generate unit tests for your widgets.
Not quite
The Widget Inspector is for visualization and debugging, not test generation.
-
Visualize your widget tree, select widgets to view their properties, and jump to source code.
That's right!
The Widget Inspector lets you explore your app's structure, inspect widget properties, and navigate to the corresponding source code.
-
Deploy your app directly to the app store.
Not quite
Deployment is handled separately; the Widget Inspector is for debugging.
-
Edit your app's theme colors and typography.
Not quite
Theme editing requires code changes; the Widget Inspector is for inspecting the current state.
Unless stated otherwise, the documentation on this site reflects Flutter 3.38.6. Page last updated on 2026-1-13. View source or report an issue.